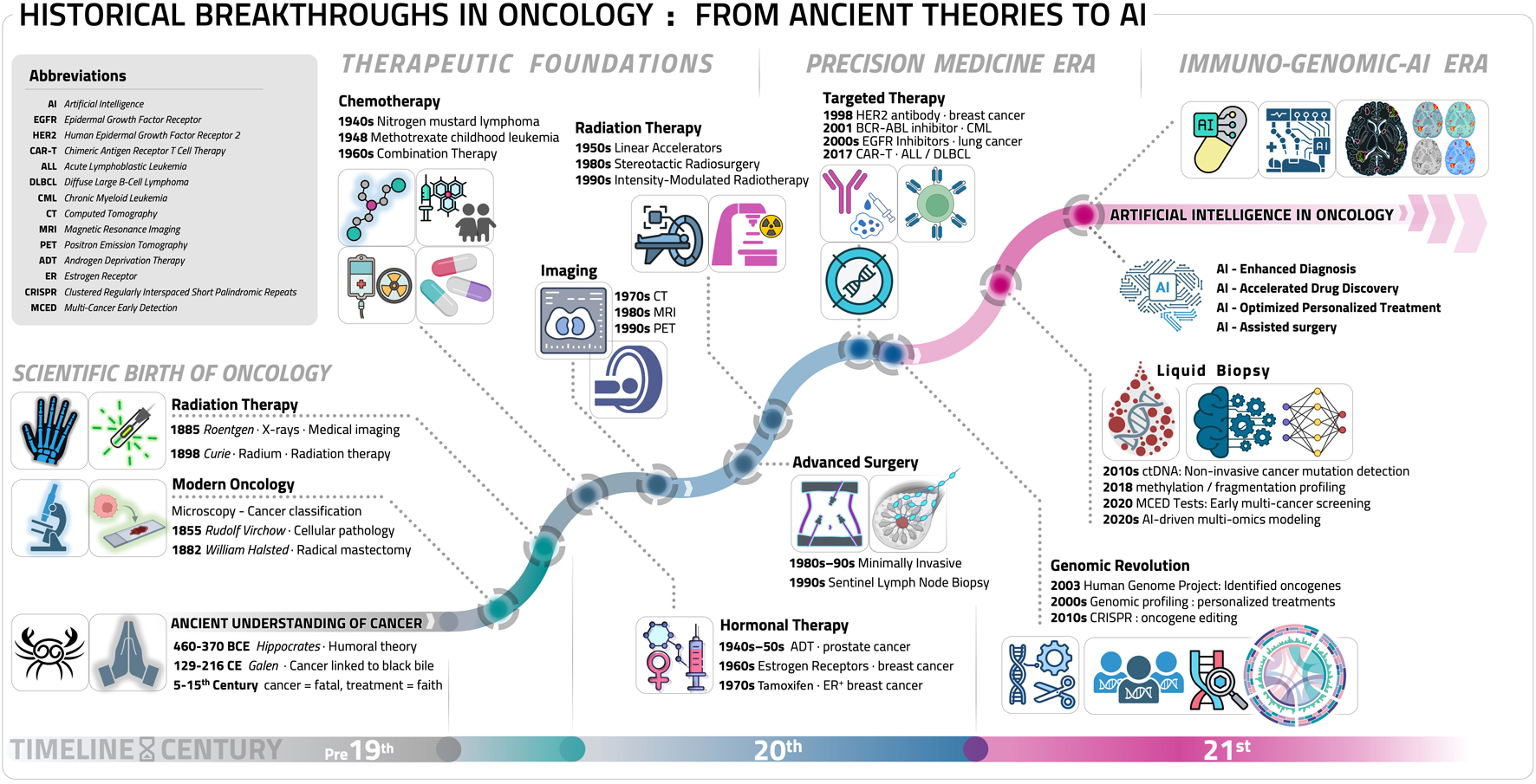
Figure 1. Key milestones in oncology: a chronological artificial intelligence (AI) perspective. This timeline diagram illustrates the major milestone breakthroughs in oncology, spanning from ancient theories to cutting-edge innovations: ancient understanding of cancer (pre-19th century), the birth of modern oncology (19th century), radiation therapy (late 19th - early 20th century), chemotherapy (mid-20th century), hormonal therapy (20th century), advances in surgical oncology: minimally invasive techniques (20th century), radiation therapy innovations (20th - 21st century), targeted therapy: precision medicine (late 20th - 21st century), immunotherapy: a new era in cancer treatment (21st century), genomic revolution: transforming cancer diagnosis and treatment (21st century), liquid biopsy and early detection (21st century), AI in oncology: transforming cancer care (21st century). Some elements in this figure, including specific icons and biological illustrations, were created using BioRender (BioRender.com).