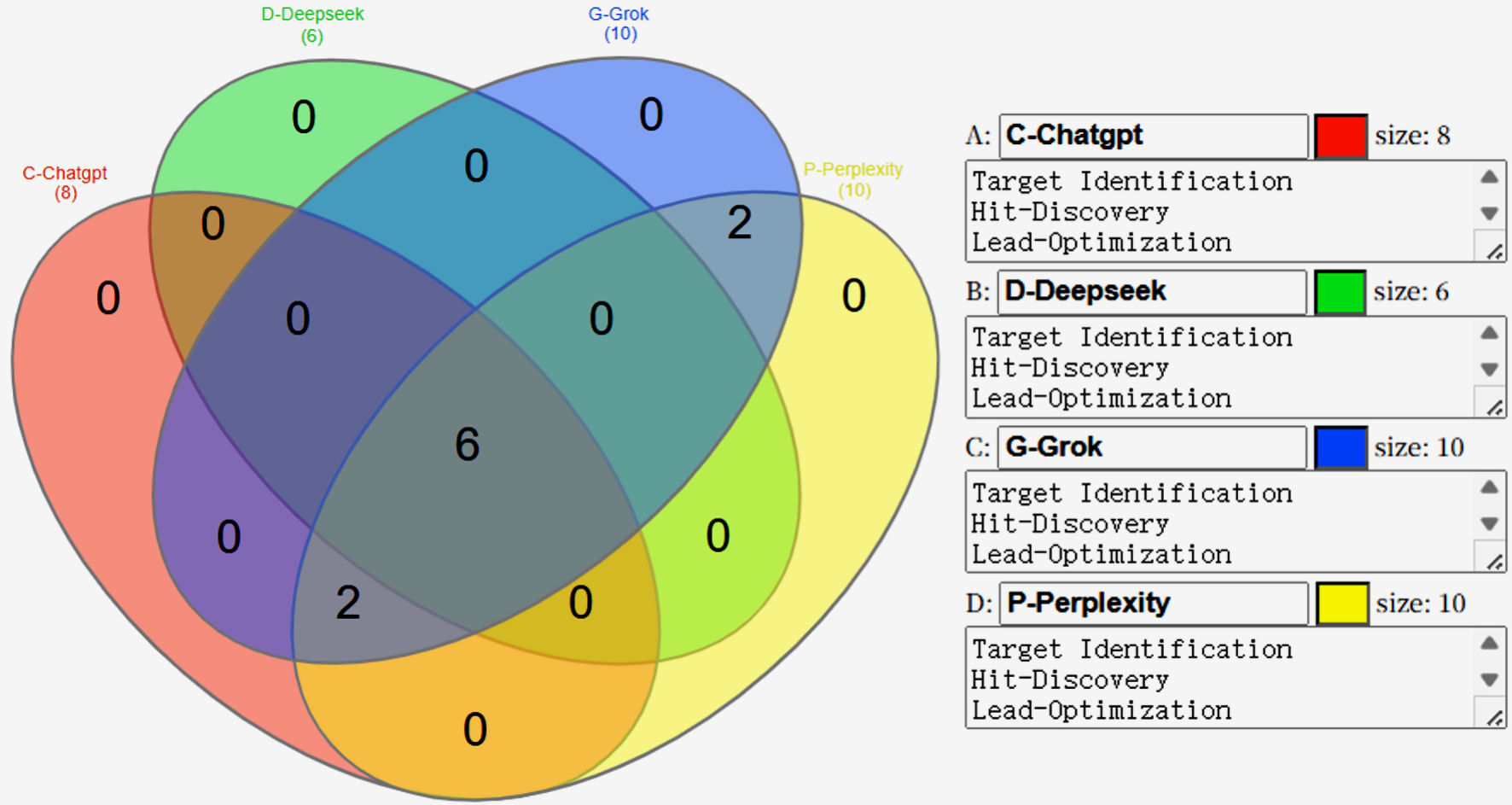
Figure 1. Comparison of the functional capabilities of four AI platforms. Venn diagram illustrating the overlap of identified items among four AI tools: C-ChatGPT (red, eight items), D-DeepSeek (green, six items), G-Grok (blue, 10 items), and P-Perplexity (yellow, 10 items). The central intersection (six items) represents elements common to all four tools. Two additional overlaps are observed between G-Grok and P-Perplexity (two items) and between C-ChatGPT and G-Grok (two items). All other pairwise or triple intersections contain no shared items (0). This visualization highlights the degree of consensus and uniqueness among the AI outputs, emphasizing the core set of commonly identified elements across platforms.
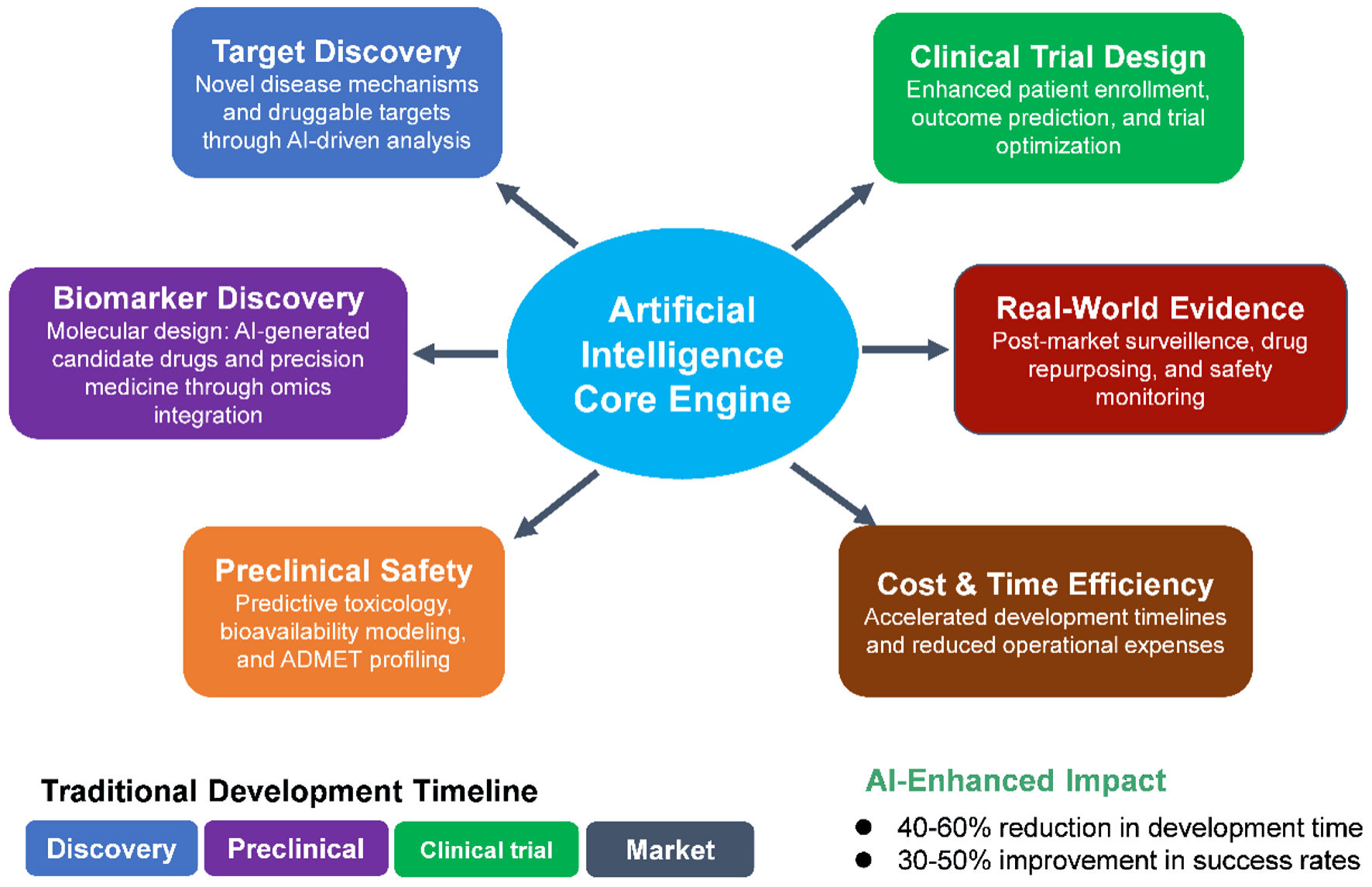
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the AI core engine’s role across the drug development pipeline. In the discovery phase, AI enables target discovery by uncovering novel disease mechanisms and identifying druggable targets through advanced computational analysis. Biomarker discovery integrates multi-omics datasets to design molecular candidates and facilitate precision medicine approaches. In the preclinical stage, AI enhances preclinical safety via predictive toxicology, bioavailability modeling, and absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) profiling, reducing reliance on extensive in vivo testing. During clinical trials, AI improves clinical trial design by optimizing patient selection, predicting outcomes, and refining trial protocols. In the market phase, AI drives RWE generation for post-market surveillance, drug repurposing, and proactive safety monitoring. Across all stages, AI delivers cost and time efficiency through accelerated development timelines, improved decision-making, and reduced operational expenses. Color coding indicates phase categories: discovery (blue), preclinical (orange), clinical trial (green), and market (red/brown). AI: artificial intelligence; RWE: real-world evidence.

