The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Accelerating Drug Discovery and Development
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/aicm8Keywords:
Artificial intelligence, Drug discovery, Machine learning, Clinical trials, Biomarker discovery, Molecular synthesis, RWE, Pharmaceutical innovationAbstract
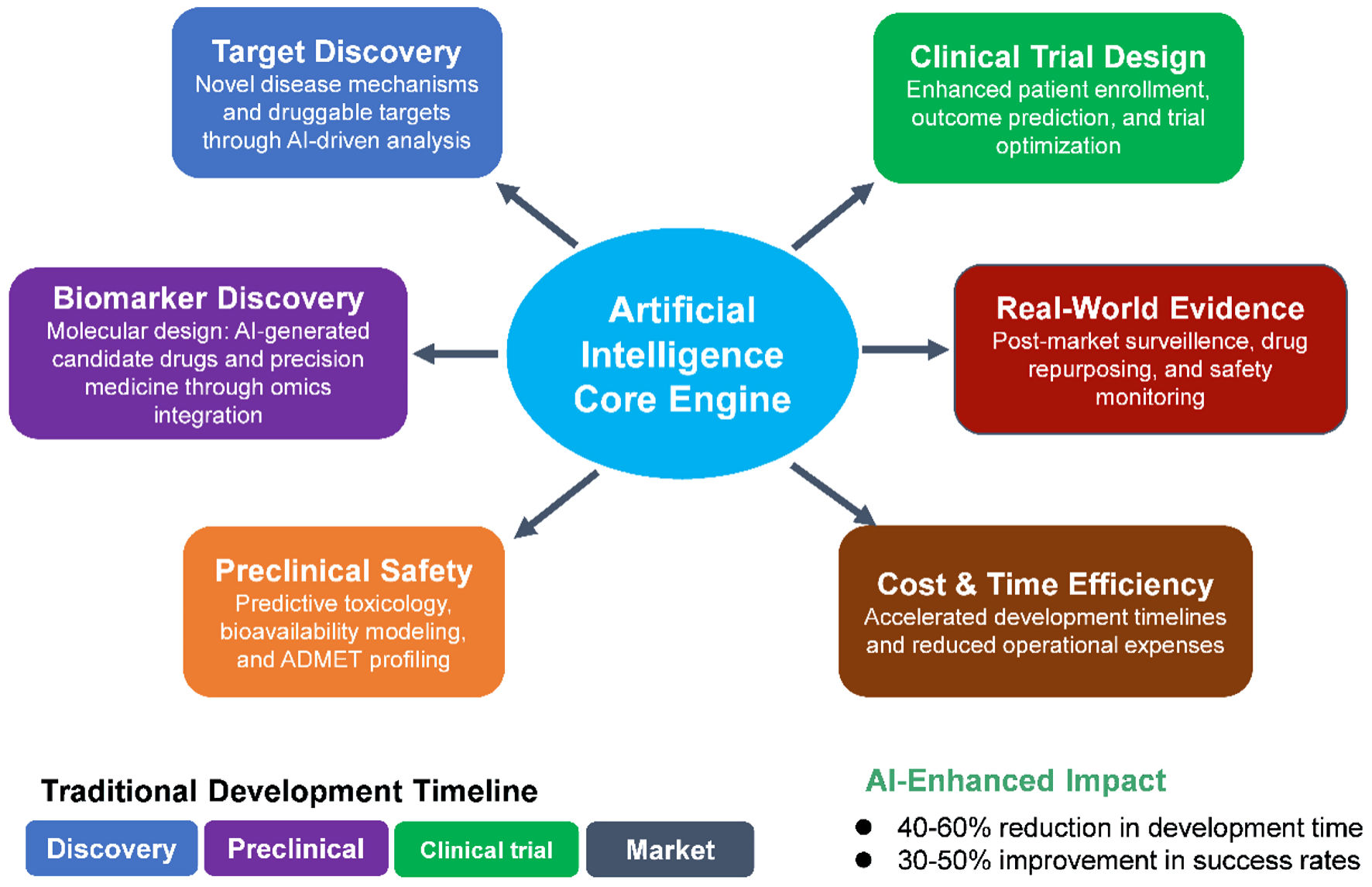
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly reshaping the pharmaceutical industry through its impact in the way drugs are discovered, developed, and delivered. Traditionally, drug development has been a lengthy, expensive, and failure-prone process, often requiring over a decade and billions of dollars to bring a single therapy to market. AI has the potential to address some of these inefficiencies by supporting faster, more data-driven decision-making in certain areas across the research and development (R&D) pipeline. This review summarizes ten key domains where AI applications are emerging, with varying degrees of demonstrated impact: 1) target identification; 2) hit discovery; 3) lead optimization; 4) preclinical modeling; 5) clinical trial design and stratification; 6) post-marketing surveillance and real-world evidence generation; 7) biomarker discovery; 8) molecular synthesis automation; 9) cost and time reduction; and 10) regulatory decision support. AI techniques - including machine learning, natural language processing, deep learning, and generative models - have shown capability in accelerating in silico screening, predicting pharmacokinetic and toxicity profiles, simulating clinical trials, and optimizing molecular design. Additionally, AI is enabling dynamic clinical trial designs, synthetic control arms, and automated patient matching, improving trial success rates. Through automated synthesis planning and robotic chemistry, AI reduces the cycle time from hypothesis to compound validation. Post-market, AI enhances pharmacovigilance by mining electronic health records and social media to detect adverse drug events earlier than traditional systems. As regulatory agencies increasingly accept AI-derived evidence, the pharmaceutical landscape is transitioning toward more efficient, scalable, and personalized drug development pathways. Despite its momentum, challenges remain, such as data bias, model transparency, and regulatory harmonization. This review underscores AI’s potential role in shaping the future of therapeutic innovation and highlights the areas that must be addressed to fully realize its potential.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






